Are we in need for the discovery of the HIV-AIDS Vaccine? #biotechnology #biochemistry #vaccines #HIV #AIDS #ipumusings
Are we in need for the discovery of the HIV-AIDS Vaccine?
Author: Priyansh Anand
ABSTRACT
Vaccines are vital requirements for protective HIV-inflamed adults from increasingly preventable diseases. However, neglected possibilities for vaccination amongst HIV-inflamed men and women persist, possibly because of issues concerning the protection and efficacy of vaccines, in addition to the converting nature of vaccine guidelines. In addition, the ideal timing of vaccination amongst HIV-inflamed adults with regard to HIV degree and receipt of antiretroviral remedy stay crucial questions. This article presents an evaluation of the present-day suggestions concerning vaccines amongst HIV-inflamed adults and a complete precis of the evidence-primarily based totally on the literature of the blessings and dangers of vaccines amongst this inclined population.
INTRODUCTION
Viruses are small segments of nucleic acid with a protein or lipoprotein coat that calls for host sources for his or her replication. Typically, a deadly disease enters a cell through a cell-floor receptor for which it has an affinity and preempts cell biosynthetic machinery to duplicate all additives of itself, consisting of its genome. This genome replication step is regularly error-prone, generating several mutations. Because big numbers of recent viral particles (virions) are produced in a replication cycle, many one of kind mutants with personal survival benefits can be decided on for the capacity to propagate maximum efficaciously withinside the host.
A virus is much more likely to thrive if it does now no longer kill its host, as sustained coexistence with inside the host favours the virus's survival and unfold. However, the mutability of the viral genome every now and then offers upward thrust to deadly variations that do now no longer agree to this country of equilibrium with their host. If such mutants purpose the early loss of life in their host, survival of the virus calls for that it unfolds to new hosts rapidly. Among the different survival techniques to be had to viruses is a protracted latency length earlier than excessive illness, for the duration of which era the host may skipping the virus to others unknowingly, as withinside the case of HIV.
One extra method utilised by viruses is facile transmission, inclusive of influenza and the smallpox virus, where the contamination is successfully transferred for the duration of even a quick acute illness. The lifestyles cycle of a few viruses pathogenic for humans, inclusive of WNV, might also encompass nonhuman hosts, providing them with extra reservoirs. Together with nonspecific defence mechanisms, numerous unique immune effector mechanisms save you or get rid of maximum viral infections. Passage across the mucosa of the respiratory, genitourinary, or gastrointestinal tracts bills for maximum times of viral transmission. Entrance of the virus might also arise thru broken skin, normally because of an insect chew or puncture wound.
The final results of this contamination rely upon the way to efficaciously the host’s protecting mechanisms face up to the offensive tactics of the virus. The innate immune reaction to viral contamination primarily starts with the popularity of pathogen-related molecular patterns (PAMPs) and ends in the technology of antiviral eff sectors. For example, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules and different virus-unique systems are detected via way of means of one of numerous PAMP receptors, inducing the expression of the kind interferons (IFN- and IFN- ), the meeting of intracellular inflammasome complexes, and the activation of NK cells.
Type I interferons can result in an antiviral reaction or resistance to viral replication via way of means of binding to the IFN-receptor, thereby activating the JAK-STAT pathway and the manufacturing of the latest transcripts, one in all which encodes an enzyme that ends in viral RNA degradation.
IFN- binding additionally induces ds R NA-based protein kinase (PKR), which ends up in the inactivation of protein synthesis, therefore blockading viral replication in inflamed cells. The binding of kind interferon to NK cells induces lytic pastime, making they may be very powerful in killing virally inflamed cells. This pastime is more advantageous via way of means of IL-12, a cytokine this is produced via way of means of dendritic cells very early withinside the reaction to viral infection.
NEUTRALISATION OF DIFFERENT VIRUSES
Antibodies specific for viral floor antigens are often critical in containing the unfold of an endemic all through acute contamination and in defensive in opposition to reinfection. Antibodies are specifically effective if they're localized on the web website online of viral entry into the frame and in the event that they bind to key viral floor structures, interfering with their cap potential to connect to host cells. For example, influenza virus binds to sialic acid residues in mobileular membrane glycoproteins and glycolipids, rhinovirus binds to intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs), and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) binds to kind 2 supplement receptors on B cells. The gain of the attenuated oral polio vaccine mentioned later in this chapter, is that it induces the production of secretory IgA, which correctly blocks the attachment of poliovirus to epithelial cells lining the gastrointestinal tract.
Viral neutralization via way of means of antibody every so often includes mechanisms that perform after viral attachment to host cells. For example, antibodies might also additionally block viral penetration via way of means of binding to epitopes which might be vital to mediate fusion of the viral envelope with the plasma membrane. If the triggered antibody is of a supplement-activating isotype, lysis of enveloped virions can ensue. Antibody or supplement also can agglutinate viral debris and feature as an opsonizing agent to facilitate C3b-receptor-mediated phagocytosis of the unfastened virions.
Despite their confined genome size, some viruses encode proteins that intervene with innate and adaptive tiers of host protection. Presumably, the benefit of such proteins is they permit viruses to copy greater efficaciously amid host antiviral defences. As defined above, the induction of kind I interferon is primary innate protection in opposition to viral infection, however, a few viruses have advanced techniques to prevent the movement of IFN- . These consist of the hepatitis C virus, which has been proven to conquer the antiviral effect of the interferons through blocking off or inhibiting the movement of PKR. Another mechanism for evading host responses is inhibition of antigen presentation through inflamed host cells. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) produces an immediate-early protein (synthesized quickly after viral replication) that very efficaciously inhibits the human transporter molecule wanted for antigen processing. Inhibition of TAP blocks antigen transport to magnificence I MHC molecules in HSV-inflamed cells, consequently stopping the presentation of viral antigen to CD8 + T cells. This consequences withinside the trapping of empty magnificence I MHC molecules withinside the endoplasmic reticulum and effectively shuts down a CD8+ T-mobileular reaction to HSV-inflamed cells. Likewise, adenoviruses and cyto megalo virus (CMV) use awesome molecular mechanisms to lessen the floor expression of sophistication I MHC molecules, once more inhibiting antigen presentation to CD8 T cells. Other viruses, which includes the measles virus and HIV, lessen tiers of sophistication II MHC molecules at the floor, consequently blocking off the feature of antigen-specific antiviral helper T cells.
Complement activation is any other of the antibody-mediated destruction pathways of viruses, ensuing in opsonization and removal of the virus through phagocytic cells. A range of viruses, which includes the vaccinia virus, prevent supplement-mediated destruction through secreting a protein that binds to the C4b supplement thing, inhibiting the classical supplement pathway. HSV additionally makes a glycoprotein thing that binds to the C3b supplement thing, inhibiting each of the classical and opportunity pathways.
WHY DO WE REQUIRE VACCINES?
In recent years, all other forms of immunodeficiency have been overshadowed by an epidemic of severe immunodeficiency caused by the infectious agent called human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). HIV causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and was first recognized as opportunistic infections in a cluster of individuals on both coasts of the United States in June 1981. This group of patients displayed unusual infections, including the opportunistic fungal pathogen Pneumocystis carinii, which causes P.carinii pneumonia (PCP) in people with immunodeficiency. Previously, these infections were limited primarily to individuals taking immunosuppressive drugs. In addition to PCP, some of those early patients had Kaposi’s sarcoma, an extremely rare skin tumour, as well as others, rarely encountered opportunistic infections. A more complete evaluation showed that all patients had a common marked deficiency in cell-mediated immune responses and a significant decrease in the subpopulation of T cells that carry the CD4 marker (T helper cells). When epidemiologists examined the background of the first patients with this new syndrome, they found that the majority were homosexual males. In those early days before we knew the cause or transmission route, and as the number of AIDS cases climbed throughout the world, people thought to be at the highest risk for AIDS were homosexual males, promiscuous heterosexual individuals of either sex and their partners, intravenous drug users, people who received blood or blood products prior to 1985, and infants born to HIV-infected mothers. We now know that all these initial patients had intimate contact with an HIV-infected individual or exposure to HIV-tainted blood.
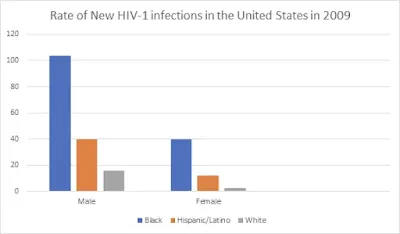
Since its discovery in the early 1980s, AIDS has increased to epidemic proportions throughout the world. As of December 2011, approximately 34 million people were living with HIV infection, 1.3 million in the United States. Although reporting of AIDS cases is mandatory in the United States, many states do not require reporting of cases of HIV infection that have not yet progressed to AIDS, making the count of HIV-infected individuals an estimate. The demographic profile of new HIV infections is evolving in the United States, where racial and ethnic minorities, especially men, are being disproportionately affected.
The toll of HIV/AIDS in the United States is dwarfed by figures for other parts of the world. The global distribution of those afflicted with HIV. In sub- Saharan Africa, the region most affected, an estimated 23.5 million people were living with HIV at the end of 2010, and another 4 million were in South and Southeast Asia. Epidemiologic statistics estimate that more than 24 million people worldwide have died from AIDS since the beginning of the epidemic, leaving millions of children orphaned. Despite a better understanding of how HIV is transmitted, estimates indicate the occurrence of 2.5 million new HIV infections in 2011, amounting to almost 7,000 new infections each day! Now the good news: rates of new HIV infections decreased by 20% worldwide in 2011 compared to 2001, and access to life-saving drugs has significantly expanded. These gains are attributable partly to the United Nations Declaration of Commitment on HIV/AIDS, signed in 2001, which has paved the way for stepped-up prevention and education programs around the world as well as expanded drug access programs. Of course, this has also led to climbing numbers of individuals living with AIDS, as the period of time from onset of AIDS to opportunistic infection lengthens. Yet, there is still no indication of an end to the epidemic.
IDEAS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF VACCINES FOR HIV-AIDS 1
Vaccines ought to be administered at or quickly after the time of HIV contamination due to the fact they may be only earlier than the onset of vast immunosuppression (i.e., quickly after HIV prognosis amongst early-recognized sufferers), and preferably given earlier than ability exposures. Vaccines advocated consist of influenza, pneumococcal, HBV, and tetanus-diphtheria-pertussis (Tdap). HAV, meningococcal, and HPV vaccines are recommended amongst HIV sufferers who've extra threat elements or are inside particular age groups. Live viral vaccines, along with measles-mumps-rubella (MMR), varicella, and zoster may be taken into consideration for at-threat HIV sufferers who're clinically solid and feature low degree immunosuppression (CD4 ≥2 hundred cells/mm3). The measles-mumps-rubella-varicella (MMRV) vaccine ought to now no longer be administered because it has now no longer been evaluated in HIV sufferers and incorporates seven instances greater varicella antigens than the monovalent vaccine, for this reason, might also additionally pose a protection concern. Current pointers now no longer suggest Haemophilus influenzae b vaccine (Hib) for adults with HIV contamination. Although HIV-inflamed folks with superior ailment have a better threat of contamination, the general occurrence is low, and maximum H. influenza instances are because of non-typeable lines for which the vaccine isn't protective.
CONCLUSION
Some already argue that lots of the cash committed to growing an HIV vaccine are wasted due to the fact the epidemic may be managed with the concerted use of the growing multitude of different prevention tools. In his deal with the AIDS Vaccine 2012 assembly in Boston, Dr Anthony Fauci, the Director of the NIAID, stated that it could be feasible to manipulate the AIDS epidemic with the growing suite of different prevention modalities. However, he argued that renovation of manipulating over a long time can also additionally require a preventive vaccine, and removal or eradication of this ailment will virtually require a vaccine because any virus or disease don’t need much time to become a pandemic around the world, just like SARS-COV 2 Virus, and vanish out whole the humanity from the earth so there is a need for the development of the vaccine because it produces a shield and a strong immunity against any virus. This is due to inherent problems with continued, big-scale countrywide efforts in addition to man or woman compliance over a protracted time. Furthermore, the no-vaccine method to manipulate the HIV epidemic comes with an exceptionally big and rarely stated cost. The renovation of an extensive HIV manipulates attempt primarily based totally on steady adherence to personally directed prevention modalities, with the extended antiretroviral remedy of prevention failures, will divert widespread assets wanted for improvement withinside the poorest international locations withinside the international condemning a big part of the international's populace to grinding poverty for many years if now no longer centuries to come. This epidemic can also additionally rework a few whole societies into HIV-manipulate economies, denying big numbers of humans destiny improvement in their innovative potential. This is unconscionable. HIV/AIDS have to be eliminated; this isn't always an ailment that we need to peer end up a usual a part of human existence. The international can't be denied an HIV vaccine. But its improvement would require higher and greater in-depth preclinical research.
REFERENCES
📌 Kuby Immunology, Seventh Edition, W. H. Freeman and Company • New York by Judith A. Owen, Jenni Punt, Sharon A. Stanford
📌 HIV Vaccine Development: Strategies for Preclinical and Clinical Investigation (weblink)
📌 Biotechnology- A problem Approach, Pathfinder Publication by Pranav Kumar, Praveen Verma, Usha Mina